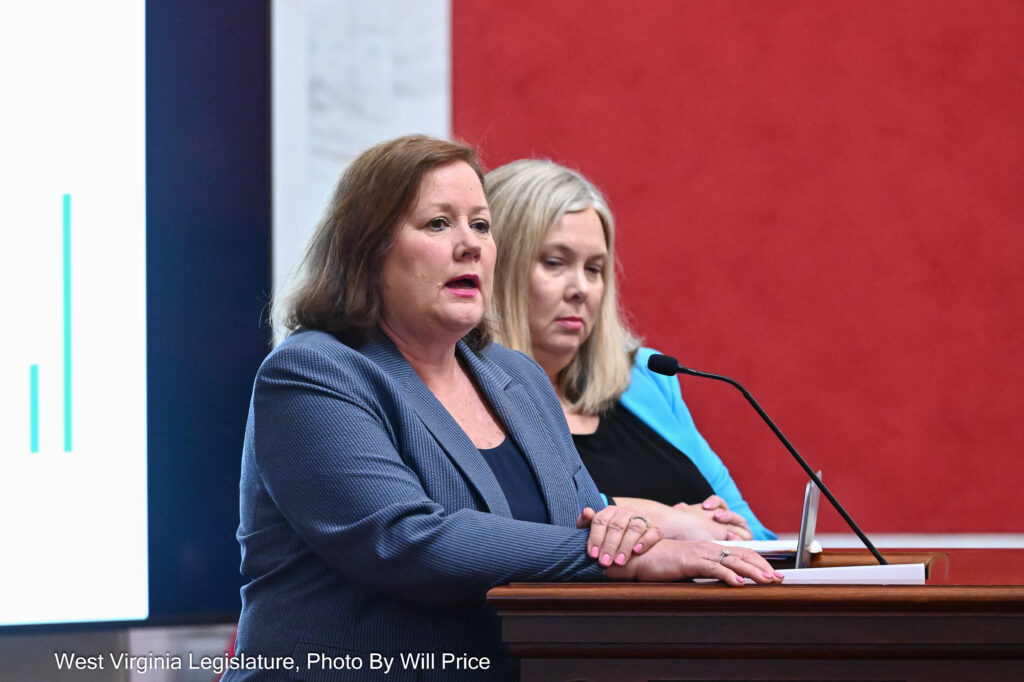
Lawmakers asked questions of state health leaders about the state’s Intellectual and Developmental Disabilities (IDD) Waiver program Monday. It allows people with disabilities to live outside hospitals and institutions by connecting people with disabilities with resources like home health care workers and financial support.
After a more than $10 million decrease in the line item in the state’s budget for the IDD waiver program, advocates and providers alike have been sounding the alarm.
In 2023, the previous West Virginia Department of Health and Human Resources (DHHR), Bureau for Medical Services contracted with Myers and Staffer, an actuary firm, to conduct a “rates” study of the Aged and Disabled Waiver, and Personal Care Services programs.
The study recommended a $6.5 million rate increase for the IDD waiver program to hire and retain direct care professionals.
Cynthia Persily, secretary of the West Virginia Department of Human Services, gave a presentation on the state’s Medicaid waiver program during a meeting of the Joint Health Committee on Monday.
The committee, led by Del. Amy Summers, R-Taylor, requested that Persily present documentation of Medicaid expenditures from the past two years, itemized by state allocation and federal match funding.
During her presentation, Persily said there have been a lot of changes during those two budget years, including changes to the federal match rate for state dollars.
“Please note that this crosses two state budget years, as well as two federal budget years,” Persily said. “As well as many changes in the federal match rate for state dollars and Medicaid, as well as a number of changes in enrollment during the unwind from the public health emergency and change to the supplemental match that occurred during that time.”
Persily said the line items for requested or authorized services are much greater than the actual services billed and reimbursed.
“There are many reasons for this, including services not being used by providers or clients during the pandemic,” Persily said. “Those years that we are looking at include the pandemic, obviously, there was a lack of services in some cases being provided for instant day programs, in home services and others may have been cut back.”
Persily testified that before the pandemic, the then-DHHR was “good at balancing” the amount of appropriation with authorized services and reimbursing services.
“During the pandemic, there were many reasons that funds were not spent as noted,” Persily said.
Before and during the pandemic, Persily testified that the previous DHHR administration would use leftover funds to fund what she called “pressing costs.”
“What is important to note is that leftover funds in the past were used in previous DHHR administrations and especially during the pandemic, to fund other pressing costs across the one DHHR, including contract nursing services at state hospitals and nursing homes, as well as COVID testing through the Bureau for Public Health, Medicaid contracts services that rose during the increased enrollment during the pandemic, self-funding of legislative mandates and appropriations and others,” Persily said.
According to Persily, this was common practice in the department before it was split into three separate departments by an act of the legislature last year.
“Through line iteming the Medicaid and waiver budgets, these between department transfers will no longer take place,” Persily said. “In addition, we have very little authority to move funds across categories within that department. So that practice will lead to enhanced transparency on where funds are spent.”
In a statement published on March 12, Sen. Eric Tarr, R-Putnam, chair of Senate Finance said his committee broke down much, but not all of Human Services in subsections and restricted the ability to transfer funds outside of those subsections in the Fiscal Year 2025 state budget.
On the final day of the regular session, Tarr amended budget cuts for individuals with disabilities into the final budget, he said, in an effort to increase transparency on the state health department’s spending.
In 2023, the IDD Waiver budget line item was $108,541,736. In this year’s budget, the IDD Waiver program was allotted $97,687,562 — a decrease of more than $10.8 million.
That budget action has since spurred action from families, individuals and advocates for people with intellectual and developmental disabilities, including a rally at the capitol on Sunday afternoon.
Advocates and families cite concerns about an already struggling system. IDD service providers like EnCircle, whose CEO, Ray Ratke, also testified Monday, are struggling to stay afloat.
“We’re currently serving 27 individuals and that has been primarily a result and really only a result of the difficulties we have in staffing group homes,” Ratke said.
EnCircle took over seven Stonebrook group homes in Martinsburg in 2020. Ratke said they were excited to expand from Virginia to West Virginia.
“In Virginia, we operate schools for kids with special needs, and we operate treatment foster care,” Ratke said. “And we were looking forward to the possibility of opening schools here in West Virginia and moving into foster care as well.”
Ratke said 14 of those 27 West Virginia individuals EnCircle serves don’t have anywhere else to go or a family that is willing or able to take them in.
“But for basically everybody we serve, they consider the home their home, and it’s not an institution, it is a home,” Ratke said.
According to Ratke, in Martinsburg, people can drive a few minutes into another state or down the street to a gas station and make more money than working as a direct care worker.
In 2020, EnCircle’s starting salary was about $9 per hour. They increased that starting salary to $13 per hour thanks to the American Rescue Plan (ARPA) funding.
According to Persily, beginning in 2021 and continuing through 2023, ARPA dollars were approved by Gov. Jim Justice to be used to provide a 50 percent increase in rates to waiver programs with the understanding that 85 percent of those increases were to be passed on directly to the direct care workforce by the businesses that accepted those funds.
“Organizations who received these funds attested their agreement to this requirement,” Persily said. “They were also notified that they had until March 31 of 2025 to utilize these funds for direct care workers and other costs, carrying them through fiscal year 2024 And the majority of fiscal year 2025.”
Ratke said he was hopeful that wage increase due to ARPA funding would help attract and retain workers
“We continue to be competing with Sheetz and Target and fast-food providers,” Ratke said. “And all of those are worthwhile businesses but that’s who we’re competing with in terms of salaries.”
Persily said the total increased reimbursement that was provided to waiver providers totaled nearly $390 million.
The Bureau for Medical Services announced Friday that they would begin audits of these providers to ensure that funds were spent appropriately and that funds will be spent by March 31, 2025.
Ratke said EnCircle is facing a loss of more than a million dollars on the six group homes they operate in West Virginia.
“We’re going to lose $1.2 million,” Ratke said. “When I say we’re not alone, we hear of other providers who are in the same or similar position we had and have reserves as being 136-year-old organization, we have reserves that we can bring to bear and shore up and pay staff, but we can’t sustain that long term.”
Commissioner of the Bureau for Medical Services, Cindy Beane, also testified to the Joint Committee on Health. She said that in 2020, the waiver waitlist was cleared of more than 1,100 individuals. However, the COVID-19 pandemic also hit around this time, and in-home services were often refused.
“At this time you had individuals and families say ‘I don’t necessarily want additional workers to come into my home’,” Beane said. “We had our day program shut. So of course our spending went down dramatically. Our spend is now retrieving and coming back up to where it should be in right-sizing.”
Beane testified that the department expects to add 90 slots to the program.
“What we will do at the end of 2024 is evaluate again to see if we can have additional slots in the program within our budget,” Beane said.
Beane also testified that while she agrees there needs to be a rate increase for direct care workers, she noted there has been a 50 percent rate increase for two consecutive years.
“We ask providers, we tell providers, you can extend this money through March of 2025,” Beane said. “Some providers have done that, some providers did not.”
She said that is one of the reasons for her department’s upcoming audit of those funds.
Tarr asked Persily and Beane why money allocated for the IDD waiver program was being used for COVID testing and contract nurse wages.
“Why would you keep the request the same for an IDD waiver rather than saying, we need less for IDD waiver, and we need more for contract nursing instead of shifting the funds to contract nursing rather than appropriate it directly?” he said.
Tarr pointed out that in previous years the department spent less than was appropriated. Persily answered that they plan a year in advance with plans to improve services or wait times.
“We’re looking at expenditures for the previous year, we’re looking at expenditures that year to date, but we are also looking at plans to reduce the waitlist plans to perhaps in the future be able to impact rates,” Persily said.
Tarr said that as chair of the finance committee, he would like to see more transparency in what is being asked of the legislature.
“So that when we spend $1 by appropriation, we know where it’s going,” Tarr said. “And it goes to the intended recipient, rather than having the bureaucracy rearrange the dollars after the legislature appropriated them.”
Persily answered that often, approved services might not be available, or a person will not receive IDD Waiver services while on vacation or during a hospital stay.
“All of those things play into why services that are authorized are always going to be higher than services that are actually received,” Persily said. “And people are estimating what services they believe, based on a, a plan of care that has been developed, they’re estimating the amount of services that people need.”
It is unclear whether IDD or other waiver line items will be reconsidered during the rumored upcoming special session.
Appalachia Health News is a project of West Virginia Public Broadcasting with support from Marshall Health.