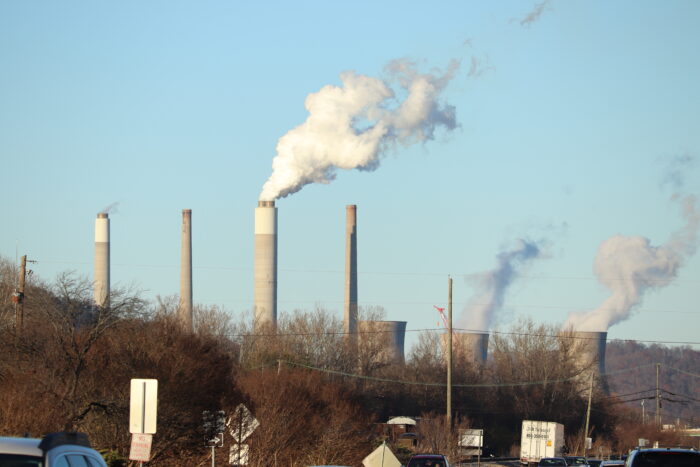
The United States joined six other countries over the weekend in a commitment to stop building new coal-fired power plants and phase out existing ones.
The United States joins the Powering Past Coal Alliance along with the Czech Republic, Cyprus, the Dominican Republic, Iceland, Kosovo and Norway.
The agreement, reached at an international climate conference in Dubai, formalizes what has already been taking place domestically and worldwide as natural gas and renewables have eroded coal’s place as the dominant fuel for electricity.
The United States has built no new coal plants in more than a decade and is on track to close half its coal capacity by 2026.
This year alone, coal has fallen below renewables and even nuclear, accounting for less than 20 percent of the nation’s electricity. Next year, it is projected to account for even less.
While it is true that China and India have been building new coal plants at a rapid pace, they are also building more wind and solar, and the pace of new coal construction is expected to slow.
The nations meeting in Dubai have attempted to achieve consensus on how to reduce carbon dioxide emissions to keep the global temperature increase to no more than 1.5 degrees Celsius.
Still, state officials are pushing back on the U.S. entry into the Powering Past Coal Alliance.
Treasurer Riley Moore, who’s running for a seat in Congress next year, criticized John Kerry, the U.S. climate envoy, and the administration policy.
“John Kerry has made the Biden Administration’s position crystal clear: they want to eliminate the coal industry worldwide regardless of the economic destruction or inflation it will cause,” Moore said in a statement Tuesday.
Moore asked Congress to reverse the U.S. commitment made at the COP28 summit in Dubai.
“I urge Congress to exert its authority and reject any attempts to commit the United States into an international climate cabal that would destroy our nation’s energy sector and overall economy,” he said.
West Virginia is the nation’s No. 2 coal producing state behind Wyoming and gets close to 90 percent of its electricity from coal, more than any other state.
West Virginia’s coal-producing neighbors, principally Pennsylvania, Ohio and Virginia, have largely shifted to natural gas from coal for their electricity.
Notably, Kosovo currently gets about the same percentage of its electricity from coal as West Virginia. The Dominican Republic gets about 10 percent, while Cyprus has never used coal.