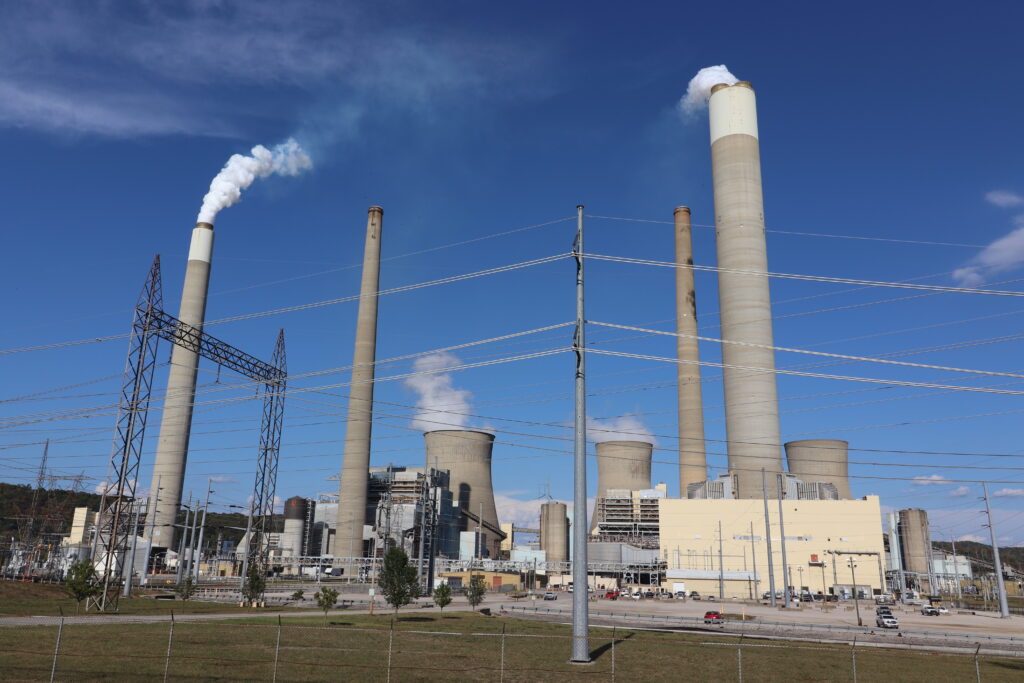
Coal’s share of electricity generation continues to shrink and the trend is irreversible, a report says.
Nearly 70,000 megawatts of coal generation will go offline from 2025 to 2030.
That’s what the Institute for Energy Economics and Financial Analysis concluded based on federal data, public announcements, financial statements and plans submitted to state regulators.
The number includes coal plants that convert to natural gas. The U.S. Energy Information Administration doesn’t count those as retirements.
The number does not include any coal plant in West Virginia. But an Appalachian Power executive recently told Virginia regulators that converting the Amos and Mountaineer plants in West Virginia is an option the company is considering.
In 2030, the report forecasts, nearly 64 percent of the nationwide coal plant capacity of 2011, the peak year, will be off the grid.